
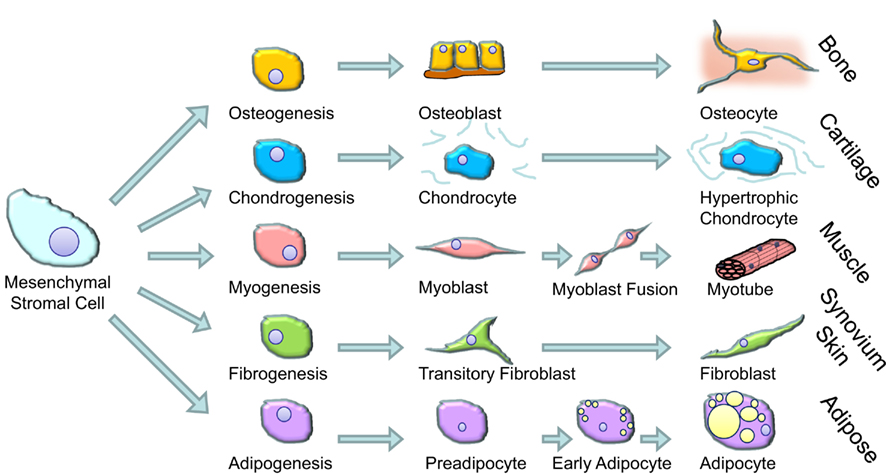
All MSCs have the ability adhere to plastic and replicate by themselves. Some stromal cells can be considered stem cells but not all therefore it can not be broadly termed a stem cell. Being a mesenchymal cell indicates an ability to develop into various other cell types and tissues such as connective tissue, blood vessels, and lymphatic tissue. These factors make it an effective tool in potential cell therapies and tissue repair. It is non-hematopoietic, multipotent, and self-replicating. A stromal cell is currently more specifically referred to as a mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC). Without a strong definition studies could not cross over or gain knowledge from each other because a stromal cell was not well defined and went by a plethora of names. Defining a stromal cell ĭefining a stromal cell is of importance because it was a source of difficulty in the past. Additionally, stromal cells play a role in inflammation responses, and controlling the amount of cells accumulating at an inflamed region of tissue. This keeps the epidermis regenerating from the bottom while the top layer of cells on the epidermis are constantly being "sloughed" off the body. Stromal cells (in the dermis layer) adjacent to the epidermis (the top layer of the skin) release growth factors that promote cell division. M-CSF, LIF ), bone marrow stromal cells have been described to be involved in human hematopoiesis and inflammatory processes. In addition, by regulating local cytokine networks (e.g. The interaction between stromal cells and tumor cells is known to play a major role in cancer growth and progression. They also aid in differentiation of hematopoietic cells and forming necessary blood elements. Stromal cells are an important part of the body's immune response and modulate inflammation through multiple pathways. The term stromal comes from Latin stromat-, "bed covering", and Ancient Greek στρῶμα, strôma, "bed". The most common stromal cells include fibroblasts and pericytes. They are cells that support the function of the parenchymal cells of that organ. Stromal cells can become connective tissue cells of any organ, for example in the uterine mucosa ( endometrium), prostate, bone marrow, lymph node and the ovary. A small fragment ofĭefinite endometrial stroma is present.Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are differentiating cells found in abundance within bone marrow but can also be seen all around the body. The sections show stripped endometrial epithelium and stripped tubal-type epithelium. This is favored to represent endometrium with cystic atrophy. PSEUDOSTRATIFIED GLANDS WITH A MILDLY FIBROTIC STROMA AND SMALL BLOOD SMALL POLYPOID FRAGMENT OF ENDOMETRIUM WITH NONPROLIFERATIVE DILATED The sample is scant given the history of 'thickened endometrium'. MINUTE BENIGN FRAGMENT OF SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. SMALL FRAGMENTS OF NONPROLIFERATIVE ENDOMETRIAL EPITHELIUM ATTACHED TO VERY SMALL FRAGMENT OF ENDOMETRIAL STROMA.

SCANT STRIPPED NON-PROLIFERATIVE ENDOMETRIAL EPITHELIUM. MINUTE FRAGMENTS OF SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY. SCANT ENDOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. STRIPPED NONPROLIFERATIVE ENDOMETRIAL EPITHELIUM NO APPRECIABLE STROMA PRESENT. Scant benign endocervical tissue (stripped epithelium and mucosa) is present. Mitotic figures are not identified within the glands or stroma. The glands are small and round, and have a pseudostratified epithelium. The sections show small fragments of endometrium. NEGATIVE FOR HYPERPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. BENIGN STRIPPED ENDOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM. SCANT ENDOCERVICAL MUCOSA WITH REACTIVE CHANGES. BENIGN SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM WITH METAPLASTIC CHANGE. Proliferative phase endometrium - esp.the person has had several biopsy attempts and was seeded with pathogens). The exceptions are benign endometrial polyp, uterine prolapse, and possibly inflammation (e.g.If a woman is truly postmenopausal, mitoses in the glandular epithelium is pathologic until demonstrated otherwise.Ovoid (palisaded) nuclei +/- nuclear pseudostratification.Moderate quantity of eosinophilic cytoplasm.Atrophy may be associated with bleeding and therefore biopsied to rule-out hyperplasia and malignancy.Menopause typically happens at around 50 years old.The most common pattern seen in postmenopausal women.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
